免责声明:该文章个人翻译,仅做学习使用,可能存在翻译错误
全文重心15.6.2介绍了MYSQL的存储方式,对于我们了解数据库,更好地使用数据库提供了基础
The InnoDB Storage Engine
15.1.1 Benefits of Using InnoDB Tables
15.1.2 Best Practices for InnoDB Tables
15.1.3 Verifying that InnoDB is the Default Storage Engine
15.1.4 Testing and Benchmarking with InnoDB
通用存储,默认使用InnoDB,如需更换引擎,创建表时ENGINE参数指定
- 高性能
- 高可靠
key Advantage
- DML遵循ACID规则(支持事务)
- Row-level locking(行锁),和Oracle风格的一致读取可提高多用户并发性和性能。
- 聚簇索引:InnoDB表将数据放在在磁盘上,来方便基于主键优化查询。每个InnoDB表都有一个称为聚集索引( clustered index)的主键索引,该索引组织数据以最小化主键查找的I / O。
- 外键约束
| Feature | Support |
|---|---|
| B-tree indexes | Yes |
| Backup/point-in-time recovery (Implemented in the server, rather than in the storage engine.) | Yes |
| Cluster database support | No |
| Clustered indexes | Yes |
| Compressed data | Yes |
| Data caches | Yes |
| Encrypted data | Yes (Implemented in the server via encryption functions; In MySQL 5.7 and later, data-at-rest tablespace encryption is supported.) |
| Foreign key support | Yes |
| Full-text search indexes | Yes (InnoDB support for FULLTEXT indexes is available in MySQL 5.6 and later.) |
| Geospatial data type support | Yes |
| Geospatial indexing support | Yes (InnoDB support for geospatial indexing is available in MySQL 5.7 and later.) |
| Hash indexes | No (InnoDB utilizes hash indexes internally for its Adaptive Hash Index feature.) |
| Index caches | Yes |
| Locking granularity | Row |
| MVCC | Yes |
| Replication support (Implemented in the server, rather than in the storage engine.) | Yes |
| Storage limits | 64TB |
| T-tree indexes | No |
| Transactions | Yes |
| Update statistics for data dictionary | Yes |
| mysql8.0 innoDB enhancements InnoDB enhancements |
15.1.1Benefits of InnoDB Tables
- 重新启动数据库(主动or意外)后都无需执行任何特殊操作
- 拥有缓冲池(buffer pool)经常访问的数据放到内存中处理
- 设置外键,更新或删除数据,并自动更新或删除其他表中的相关数据。
- 数据损坏提示
- 设计正确的主键,会自动优化,使得where,order,group迅速
- CRUD通过自动机制(change buffering)可以对同一张表并发读写(行锁的优势),以及缓存CRUD后一起写入减少磁盘IO
- 慢查询性能优异,自适应哈希索引(Adaptive Hash Index)使得一行被多次访问时,读取更快,就像hash一样
- 支持压缩表和关联索引(associated indexes)
- 支持创建和删除索引,而对性能和可用性影响较低
- Truncating a file-per-table tablespace is very fast, and can free up disk space for the operating system to reuse, rather than freeing up space within the system tablespace that only
InnoDBcan reuse.(不知道在说什么) - DYNAMIC格式解决BLOB和长文本的存储问题
- INFORMATION_SCHEMA监视存储引擎内部信息
- 通过查询性能架构表(performance schema)来监视存储的性能
- 兼容其他引擎的table
- 处理大量数据时提高CUP效率,获得最佳性能
- 支持处理大量数据
15.1.2 Best Practices for InnoDB Tables
- 合理设置主键或者设置自动增量为主键
15.2 InnoDB and the ACID Model
15.3 InnoDB Multi-Versioning
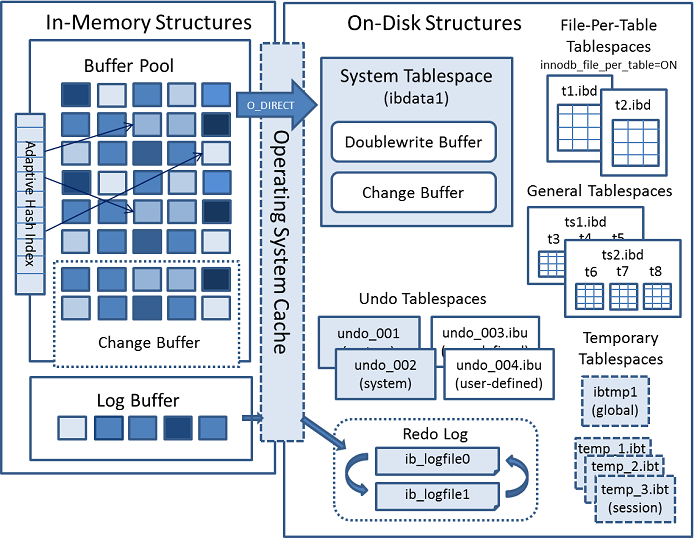
15.4 InnoDB Architecture
图示↓
15.5.1 Buffer Pool
设置buffer pool
目的:提高大容量读取操作的效率,Pool 分为多个页,容纳多行数据,页遵循LRU:latest recently used替换原则
缓冲池列表↓
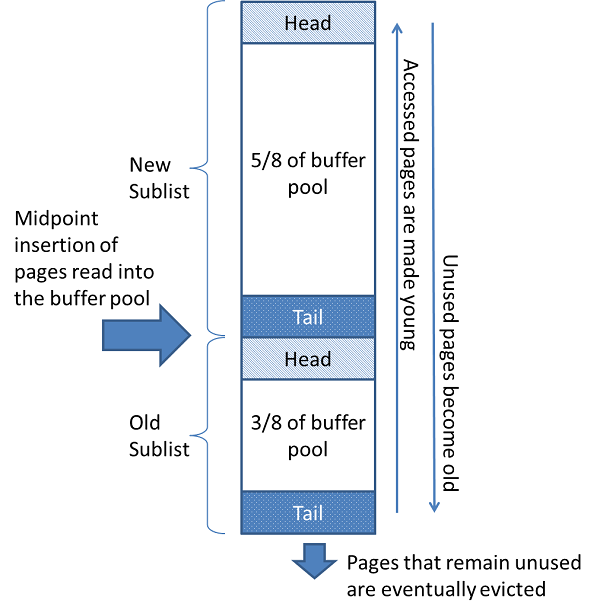
LRU使得常用的页在new sublist部分,oldsublist是不常用,其中的页会被替换
默认配置下算法具体完成
- old sublist占据3/8
- midpoint 是新旧的边界
- 新页插入midpoint位置(old头部)且可以被读(因为是用户启动的操作,例如sql query),或者加载预读
- 对old区的页操作,用户主动操作会使得页移向new区域,预读操作则不会
- 不断更新,old末位淘汰
默认情况下,用户主动操作dump操作也会把数据加载到pool中,尽管这些数据不在访问,以及预读仅访问一次的页面多次加载移到new的表头,慢慢淘汰,都存在问题
默认配置:
- 专机配置80%的内存作为buffer pool
- 将缓冲池划分,避免并发竞争
- 频繁访问的数据常驻内存
- 控制预读请求,异步将数据调到buffer pool
- 适当执行background flushing
- 配置innodb缓冲池备份,避免意外
监视buffer pool
使用
SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS
访问monitor提供的缓冲池数据
| Tpye | name | status |
|---|---|---|
| InnoDB | (见下) |
1 |
|
核心指标
Total large memory allocated 137363456//总内存
Dictionary memory allocated 464815//data+index分配内存
Buffer pool size 8192
Free buffers 6942
Database pages 1243
Old database pages 478
Modified db pages 0
Pending reads 0
Pending writes: LRU 0, flush list 0, single page 0
Pages made young 0, not young 0//移到young区页数
0.00 youngs/s, 0.00 non-youngs/s//移动速度
Pages read 1100, created 143, written 214
0.00 reads/s, 0.00 creates/s, 0.00 writes/s
//命中率指标
Buffer pool hit rate 1000 / 1000, young-making rate 0 / 1000 not 0 / 1000
//预读指标
//预读速度,预读后无效页速度,随机预读速度
Pages read ahead 0.00/s, evicted without access 0.00/s, Random read ahead 0.00/s
//LRU列表长度
LRU len: 1243, unzip_LRU len: 0
I/O sum[0]:cur[0], unzip sum[0]:cur[0]
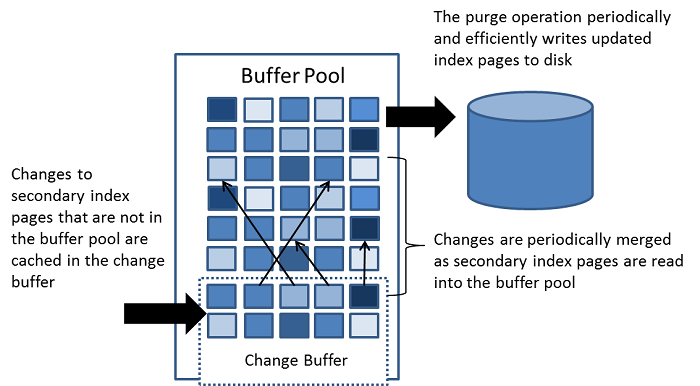
15.5.2 Change Buffer
change buffer是一种特殊的数据结构,页面不在缓冲池时,cashes会改变secondary index,当缓冲更改将在以后通过其他读操作将页面加载到缓冲池合并
15.5.3 Adptive Hash Index
15.5.4 Log Buffer
15.6.1 Tables
15.6.1.1 Creating InnoDB Tables
create table statement
CREATE TABLE t1 (a INT, b CHAR (20), PRIMARY KEY (a)) ENGINE=InnoDB;
默认配置下,默认InnoDB,则无需指定,查询配置中默认引擎指令
SELECT @@default_storage_engine
在以下情况下需要使用ENGINE=InnoDB
- use mysqldump(A Database Backup Program)
- 复制到不是innodb的server上
innodb的表和索引创建在system tablespace or file-per-table tablespace or general tablespace。当启用innodb file per table(默认启用),innodb表会被隐式创建在读了的file-per-table space。相反的禁用会创建在innodb system tablespace.使用create table … tablespace 语法在general tablespace中创建表
当你在`file-per-table tablespace 中创建表的时候,MySQL默认会在数据目录下创建.db表空间文件。在Innodb system tablespace中创建的表,由已经存在的ibdata文件创建的,该文件在MySQL data目录中,在general tablespace 中创建的表,由已经存在的general tablespace .bd文件创建,该文件可以在data 目录的内部或者外部
内部中,innodb会将每个表的entry添加到data dictionary中。entry包括,database name。例如,在数据库中创建table t1 (in test database),datadictionary 就是test/t1,当你在别的database中创建同名表不会冲突。
InnoDB tables and Row Formats
默认通过innodb default row format配置项配置默认行格式,默认值DYNAMIC.
Dynamic 和 Compressed行格式功能,比如
- 表压缩
- efficient off-page storage of column values
该功能需要innodb file per table支持
1 | SET GLOBAL innodb_file_per_table=1; |
InnoDB Tables Primary Keys
主键必须存在,并满足一个或多个条件:
- 经常索引
- 不为空
- 不重复
- 几乎不更新
1 | # The value of ID can act like a pointer between related items in different tables. |
innodb talbe properties
1 | mysql> SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM test LIKE 't%' \G; |
15.6.1.2 Creating Tables Externally
创建外键原因:
- space management
- IO优化
- 把表放置在特定性能或者容量的存储设备上(?)
创建方式:
- 使用data directionary
- CREATE TABLE … TABLESPACE Syntax
- Creating a Table in an External General Tablespace
Using the DATA DIRECTORY Clause
CREATE TABLE t1 (c1 INT PRIMARY KEY) DATA DIRECTORY = ‘/external/directory‘;
在file-per-talbe tablespaces中支持使用DATA DIRECTORY clause创建表。在file-per-table中启用innodb file per table将隐式创建表
1 | mysql> SELECT @@innodb_file_per_table; |
External
1 | mysql> USE test; |
使用须知
- external时候要确保innodb知道该目录
- (待补充)
Using CREATE TABLE … TABLESPACE Syntax
1 | CREATE TABLE t2 (c1 INT PRIMARY KEY) TABLESPACE = innodb_file_per_table |
这个方法仅仅可以用在file-per-talbe tablespaces中创建的表,并不需要enable innodb file per talbe,在其他方面,这个方法等效于create table …data directory方法,适用相同使用须知
Creating a Table in an External General Tablespace
可以在general tablespaces中依靠external directory创建表
15.6.1.3 Importing InnoDB Tables
15.6.1.4 Moving or Copying InnoDB Tables
15.6.1.5 Converting Tables from MyISAM to InnoDB
15.6.1.6 AUTO_INCREMENT Handling in InnoDB
15.6.2 Indexes
15.6.2.1 Clustered and Secondary Indexes
该章节受面试官欢迎
innodb采用聚簇索引,存储行数据,聚簇索引与主键同义(Synonymos)
- 主键(或自增列)会用作聚簇索引
- 如果没有主键则mysql会在所有列都不为null的情况下,给unique索引用作聚簇索引
- 如果以上都没有,会内部生成名为GEN_CLUST_INDEX的隐藏聚集索引
why更快
聚簇索引访问行是快速的,因为可以直接导航到所有行数据的页,如果页很大,聚簇索引相对于其他会减少IO(其他的引擎使用不同的页面来存储行数据和索引)
两者相关
在非聚簇索引中,每条记录包含主键以及指向非聚簇索引的列(个人理解,除了存储主键,主键还需要存储地址去指向row)
在聚簇索引中,利用主键的值取寻找这条记录
如果主键长则非聚簇索引使用更多空间,因此它适合使用短主键
15.6.2.2 The Physical Structure of an InnoDB Index
除了空间索引(spatial indexes),innoDB索引都是B-tree
空间索引使用R-trees(索引多维数据的专用数据结构)
索引记录存储在B树或者R树,数据结构中的叶子节点中的页中,索引页默认16K
当新的记录插入到聚簇索引中时,innodb尝试空闲页1/16供将来插入和更新索引记录
顺序插入则所得索引页约为15/16装满
乱序插入则页面容量为1/2 to 15/16
InnoDB在创建或者重建Btree时执行批量加载,成为排序索引构建(sorted index build)通过innodb fill factor 配置项定义在排序索引构建期间填充每个B-Tree页面上的空间百分比,剩余的空间将来索引增长使用
15.6.2.4 InnoDB FULLTEXT Indexes
15.6.3 Tablespaces
15.6.3.1 The System Tablespace
15.6.3.2 File-Per-Table Tablespaces
15.6.3.3 General Tablespaces
15.6.3.4 Undo Tablespaces
15.6.3.5 Temporary Tablespaces
15.6.3.6 Moving Tablespace Files While the Server is Offline
###15.6.4 Doublewrite Buffer
15.6.5 Redo Log
15.6.6 Undo Logs
](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-fulltext-index.html)